Intro: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Types of MT Systems == | == Types of MT Systems == | ||
Approaches to MT can be categorized by whether they work directly with surface words or whether they utilize some (linguistic) abstraction. | Approaches to MT can be categorized by whether they work directly with surface words or whether they utilize some (linguistic) abstraction. | ||
[[File:pyramid.png| | [[File:pyramid.png|thumb|500px|'''Vauqouis triangle.''' Illustrates the possible approaches to linguistic abstraction in MT.]] | ||
Many successful MT systems disregard any linguistic information and treat all words as unrelated, indivisible units -- these correspond to the ''direct translation'' arrow. | Many successful MT systems disregard any linguistic information and treat all words as unrelated, indivisible units -- these correspond to the ''direct translation'' arrow. | ||
Other systems perform linguistic '''analysis''' on the source side and then do '''transfer''' -- either to some abstract representation or directly to target-side surface words. In the first case, target-side '''generation''' is needed to create the surface words of the translation. | Other systems perform linguistic '''analysis''' on the source side and then do '''transfer''' -- either to some abstract representation or directly to target-side surface words. In the first case, target-side '''generation''' is needed to create the surface words of the translation. | ||
Revision as of 13:11, 31 October 2014
Ambiguity in Language
Unusual grammatical constructions with unexpected meaning can be used to (deliberately) mislead a human reader. These are called garden path sentences. Consider some of the best-known examples:
- Fat people eat accumulates.
- The horse raced past the barn fell.
- The government plans to raise taxes were defeated.
But everyday sentences actually contain countless ambiguities which humans resolve so naturally that they do not even notice them. Knowledge of the world and context are essential.
The plant is next to the bank.
- plant
- factory?
- flower?
- bank
- financial institution?
- river side?
Types of MT Systems
Approaches to MT can be categorized by whether they work directly with surface words or whether they utilize some (linguistic) abstraction.
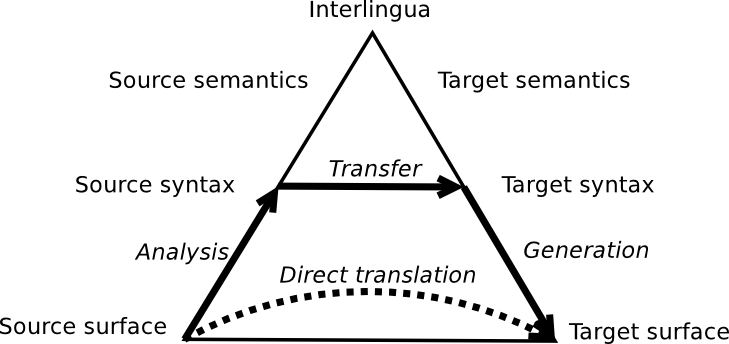
Many successful MT systems disregard any linguistic information and treat all words as unrelated, indivisible units -- these correspond to the direct translation arrow.
Other systems perform linguistic analysis on the source side and then do transfer -- either to some abstract representation or directly to target-side surface words. In the first case, target-side generation is needed to create the surface words of the translation.